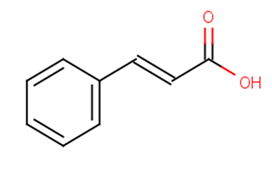
Cinnamic acid (b)
CAS No. 621-82-9
Cinnamic acid (b)( 3-Phenylacrylic acid | β-Phenylacrylic acid )
Catalog No. M20349 CAS No. 621-82-9
Cinnamic acid has potential use in cancer interventionThe concentration causing a 50% reduction of cell proliferation (IC50) ranged from 1 to 4.5 mM in glioblastoma melanoma prostate and lung carcinoma cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCinnamic acid (b)
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCinnamic acid has potential use in cancer interventionThe concentration causing a 50% reduction of cell proliferation (IC50) ranged from 1 to 4.5 mM in glioblastoma melanoma prostate and lung carcinoma cells.
-
DescriptionCinnamic acid has potential use in cancer interventionThe concentration causing a 50% reduction of cell proliferation (IC50) ranged from 1 to 4.5 mM in glioblastoma melanoma prostate and lung carcinoma cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms3-Phenylacrylic acid | β-Phenylacrylic acid
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number621-82-9
-
Formula Weight148.16
-
Molecular FormulaC9H8O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol:50 mg/mL (337.47 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)\C=C\c1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Hafizur R M Hameed A Shukrana M et al. Cinnamic acid exerts anti-diabetic activity by improving glucose tolerance in vivo and by stimulating insulin secretion in vitro[J]. Phytomedicine 2015 22(2):297-300.
molnova catalog



related products
-
1-Methyladenosine
1-Methyladenosine (M1A) belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine nucleosides.
-
4-Guanidinobutyric a...
4-Guanidinobutyric acid is an L-arginine metabolite that has been used in the intestinal transport tranport studies. It has been specifically use to human proton coupled amino acid transporters hPAT1.
-
2-Methylbutyraldehyd...
2-Methylbutanal belongs to the class of organic compounds known as short-chain aldehydes.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


